Real-time Air Quality: PurpleAir Map - Explore Now
What is the best way to visualize air quality data? This interactive tool provides a readily understandable, comprehensive overview.
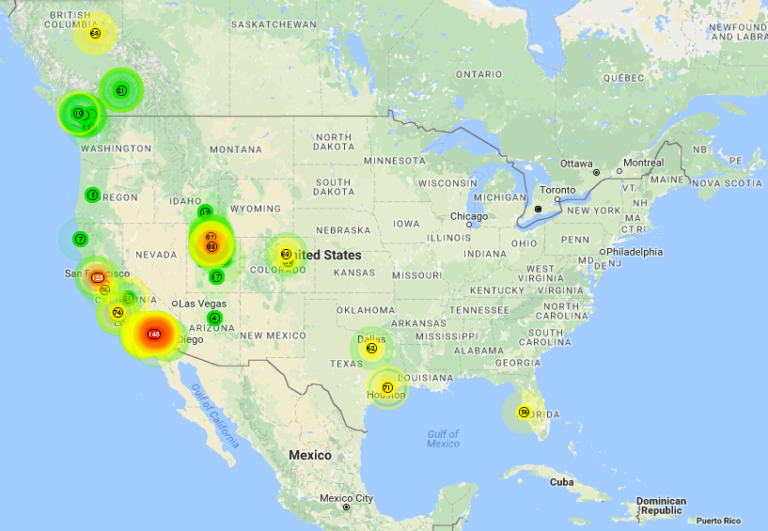
This real-time map displays air quality measurements across a given geographical area. Each location on the map corresponds to an air quality sensor, visually presenting particulate matter and other pollutants, often using color-coded gradients. These maps, updated frequently, allow for immediate observation of pollution levels, enabling users to rapidly assess the air quality in different zones.
The interactive nature of the map enables immediate insight into pollutant concentrations. This visual representation allows for swift identification of high-pollution areas, which can be crucial for public health advisories, urban planning, and individual decision-making regarding outdoor activities. Historical data overlays can further underscore trends and patterns in air quality. The map's availability and ease of use make it a critical resource for anyone needing to understand and act upon air quality information in a specific location.
Moving forward, this resource will be explored in greater detail, focusing on practical applications and interpretation strategies.
PurpleAir Map
The PurpleAir map serves as a vital tool for understanding real-time air quality. Its multifaceted nature allows for a comprehensive assessment of pollutant levels.
- Real-time data
- Geographic coverage
- Pollution levels
- Color-coded display
- Sensor network
- Data visualization
- Public access
This map's real-time data, coupled with geographic coverage, allows users to pinpoint high-pollution areas. The color-coded display provides an immediate visual understanding of pollution levels. A vast sensor network fuels the map's data, offering diverse perspectives on air quality. The visualization of pollution data enables informed decision-making, for instance, choosing healthier outdoor routes during periods of heightened pollution. Public access ensures that this valuable resource benefits a broad audience. The map connects data to location, empowering informed choice and enabling preventative action. For example, understanding elevated pollution levels near schools allows for proactive measures. Understanding pollution patterns, like seasonal variations or localized industrial emissions, is facilitated by historical data availability.
1. Real-time data
The fundamental characteristic of a PurpleAir map lies in its real-time data. This instantaneous information forms the core of the map's utility. Continuous updates from a vast network of air quality sensors furnish the map with current pollutant levels. This immediacy is crucial for identifying and responding to localized pollution spikes. A factory emission, for example, could be instantly detected and reported, enabling timely intervention.
The relevance of real-time data transcends immediate alerts. It supports informed decision-making. Knowing the current air quality enables individuals to adjust outdoor activities, parents to make choices regarding children's outdoor time, or urban planners to quickly assess potential health risks. Predictive models, drawing upon historical real-time data, can assist in anticipating pollution patterns, potentially allowing for proactive measures and early intervention. Real-time updates, combined with data on wind direction and speed, can improve the accuracy of air quality predictions.
In summary, the real-time data captured by the air quality sensor network underpinning the PurpleAir map is essential. Its immediate availability allows for prompt response to pollution events, supports informed decisions, and potentially enables preventative measures. The ongoing availability of this crucial data is a key benefit of the platform.
2. Geographic coverage
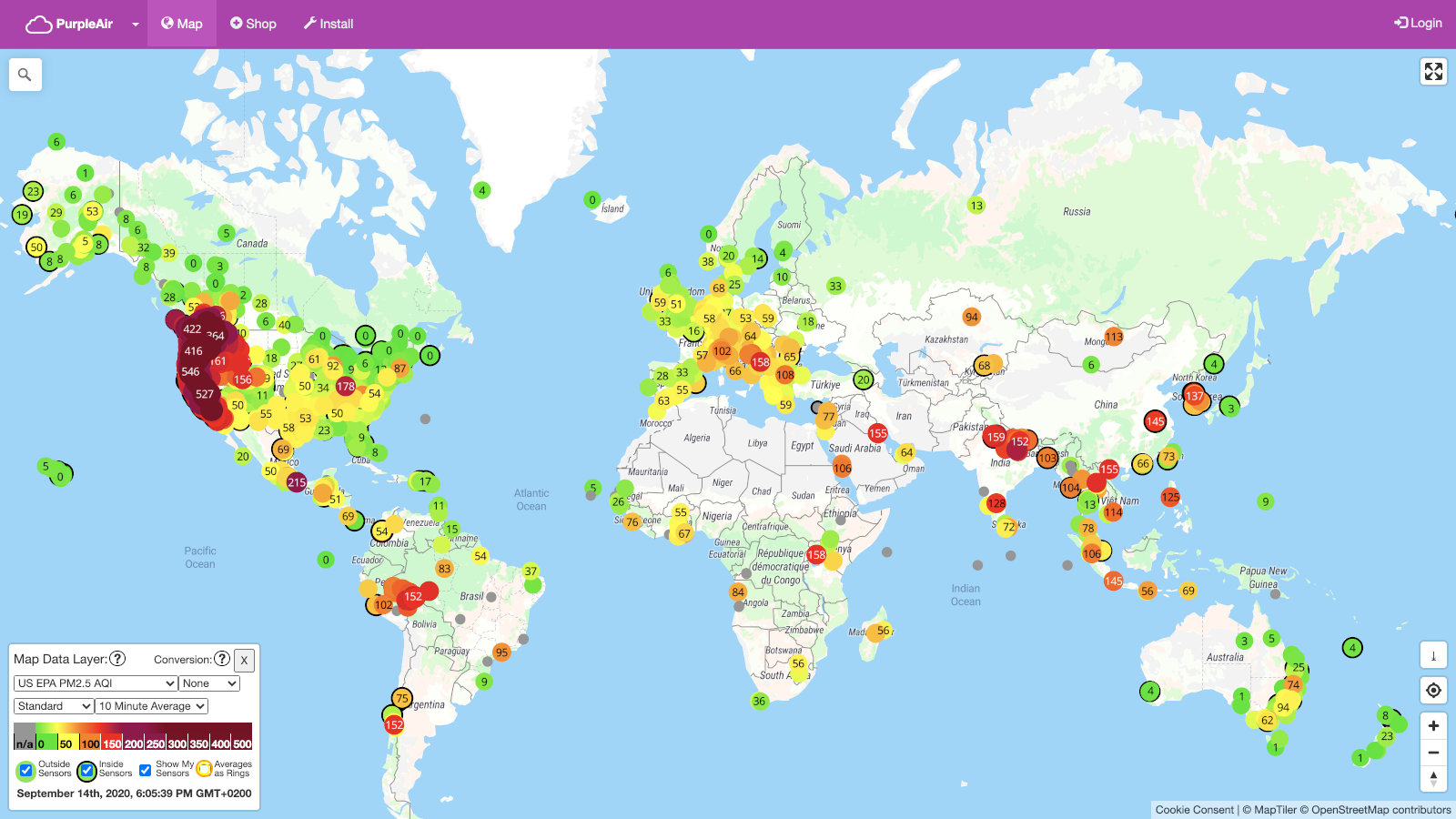
Geographic coverage on a PurpleAir map is critical to its effectiveness. The comprehensiveness of the area monitored directly impacts the map's value. A broader area allows for a more complete picture of air quality trends, potentially revealing regional patterns and larger-scale pollution issues.
- Regional Comparisons
The map facilitates comparisons between different geographical areas. This comparison, based on real-time data, can highlight disparities in pollution levels. Such distinctions might reveal whether certain industrial zones, urban centers, or even specific neighborhoods have higher pollution levels. Understanding these regional variations is instrumental in targeted pollution mitigation strategies.
- Identifying Pollution Sources
Geographic coverage enables the identification of potential pollution sources. A concentrated area of high pollution, geographically isolated from significant industrial activity, may point towards an undiscovered localized source, such as a construction site or a poorly regulated small-scale industry. This information supports targeted regulatory action.
- Spatial Correlation
The map allows for the analysis of spatial correlations between pollution levels and geographical features. This includes correlations between pollution and topography, proximity to roadways, or even land use patterns. Insights from such spatial correlations can provide a more nuanced understanding of pollution generation and dispersion.
- Real-time Monitoring of Events
Comprehensive geographic coverage allows for real-time monitoring of large-scale events. This includes pollution from wildfires, major industrial incidents, or even severe weather events. Such large-scale events can result in significant localized pollution, and the map offers immediate awareness, potentially saving lives or mitigating health risks.
In conclusion, the geographic scope of the PurpleAir map significantly influences its value. Comprehensive geographic coverage fosters deeper insights into pollution trends, sources, and events, thus empowering effective actions and improved environmental management practices. Detailed knowledge about geographical areas, coupled with the map's real-time data, allows for a more targeted and impactful approach to managing and improving air quality.
3. Pollution levels
Pollution levels are a fundamental component of the PurpleAir map. The map's value hinges on accurately representing these levels, visually displaying data for immediate understanding. Precise measurement of pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) and ozone, forms the core of the map's function. The map's color-coding system directly correlates with these levels, enabling users to readily discern areas with high pollution from those with cleaner air. This visual representation is vital for identifying pollution hotspots and understanding the geographic distribution of pollutants.
Accurate representation of pollution levels is crucial for a variety of practical applications. Public health officials use this data to issue advisories about air quality, potentially guiding individuals to take precautions, especially those with respiratory conditions. Urban planners might leverage these insights for developing strategies to reduce pollution. For instance, understanding high-pollution areas near schools informs decisions regarding air quality mitigation strategies. The rapid identification of pollution spikes enables businesses and individuals to react quickly and make better decisions, such as adjusting transportation routes, prioritizing indoor work, or cancelling outdoor events, ultimately minimizing potential health risks. Industrial facilities can utilize these maps to identify potential emission issues and prioritize control measures.
In conclusion, pollution levels are integral to the PurpleAir map's functionality. Accurate measurement and representation of these levels empower informed decisions and actions related to public health, urban planning, and environmental management. This visual representation enables timely interventions and supports effective strategies for mitigating pollution's negative impacts. The connection between the data and the visualized map fosters a more responsive and proactive approach to air quality management.
4. Color-coded display
The color-coded display on a PurpleAir map is a crucial component, transforming complex air quality data into a readily understandable visual representation. This visual approach significantly enhances the map's utility by allowing quick assessment of pollution levels across a geographic area.
- Visual Clarity and Accessibility
The color-coded system immediately conveys pollution levels. Darker shades signify higher pollution concentrations, while lighter shades indicate cleaner air. This simplified visual language enables quick comprehension by a broad audience, irrespective of technical expertise. This accessibility is vital for public health outreach and awareness campaigns.
- Instantaneous Identification of Pollution Hotspots
The color-coded scheme facilitates the rapid identification of areas experiencing elevated pollution levels. This immediate visualization is valuable in identifying potential health risks, guiding individuals in making informed choices about outdoor activities, and assisting emergency responders in targeted interventions during crises.
- Comparison and Trend Analysis
By visually comparing different regions and time periods, patterns in pollution emerge. Variations in color shades reveal trends in pollution levels, enabling the identification of seasonal fluctuations, localized pollution sources, or larger-scale environmental changes. This information can be invaluable to environmental agencies, researchers, and policymakers.
- Data Interpretation and Decision-Making
The color-coded display effectively bridges the gap between raw data and actionable insights. The visual cues simplify data interpretation, enabling individuals and organizations to make rapid judgments and decisions regarding health, safety, and resource allocation. Public health advisories and traffic management strategies can all benefit from this visual clarity.
In essence, the color-coded display on a PurpleAir map significantly enhances the effectiveness and usability of the platform. It serves as a vital tool for understanding, communicating, and responding to air quality issues across diverse geographic areas. This approach transcends purely numerical data, providing a powerful platform for informed decision-making and impactful actions.
5. Sensor network
The PurpleAir map's accuracy and utility are inextricably linked to its sensor network. This network comprises a distributed array of air quality sensors strategically positioned across various geographic locations. Each sensor continuously monitors key pollutants, capturing real-time data on particulate matter, ozone, and other relevant atmospheric components. The quality of the data visualized on the map is directly contingent on the density, distribution, and reliability of these sensors within the network. Robust sensor networks ensure comprehensive spatial coverage, which is crucial for understanding regional pollution patterns and pinpointing localized pollution sources.
The density and distribution of sensors within the network are critical. Sparse sensor networks may fail to capture localized pollution events or accurately reflect gradients in pollution levels. Dense sensor networks, on the other hand, can produce a more nuanced and complete picture, allowing for the identification of localized pollution sources that might otherwise go unnoticed. Real-world examples of the impact of sensor network design include studies demonstrating how the placement of sensors near industrial facilities or major roadways allows for the detailed tracking of emission spikes, which would be impossible with a less comprehensive network. This is particularly important in areas with significant traffic or industrial activity where targeted pollution mitigation is critical.
Understanding the sensor network's role in constructing the PurpleAir map is fundamental to evaluating its overall reliability and usefulness. A well-maintained and comprehensive sensor network directly translates to a more informative and accurate representation of air quality. The network's design choices, including sensor type, maintenance procedures, and data transmission protocols, significantly influence the map's overall performance. Inadequate or unreliable sensor networks can lead to inaccurate visualizations, potentially jeopardizing the validity of public health advisories, environmental assessments, or urban planning decisions. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of the sensor network's capabilities and limitations is essential for ensuring responsible use and interpretation of the PurpleAir map.
6. Data Visualization
Data visualization plays a critical role in the PurpleAir map. Transforming complex atmospheric data into easily digestible graphical representations is fundamental to understanding and acting upon air quality information. This visualization allows users to quickly grasp pollution patterns, identify pollution sources, and track trends, facilitating a wide range of applications from public health to urban planning.
- Spatial Representation
The map's core function is spatial visualization. By displaying air quality measurements across a geographical area, users can instantly identify pollution hotspots. Color gradients or other visual cues represent pollutant concentrations, offering a clear picture of where pollution is most prevalent. This spatial representation is crucial for pinpointing areas needing immediate attention, such as schools or hospitals located in high-pollution zones.
- Temporal Trends
Data visualization on the PurpleAir map extends beyond static spatial representations. The map often allows users to view historical data alongside current readings. Overlaid time-series graphs or animated representations reveal trends in pollution levels over time, exposing seasonal variations, daily cycles, or the impact of specific events (like industrial activity or weather patterns) on air quality. This capability aids in understanding the evolution of pollution, identifying recurring patterns, and anticipating future pollution challenges.
- Data Integration
The PurpleAir map typically integrates various data sources beyond raw sensor readings. Information about weather patterns, traffic data, or even industrial emissions can be overlaid onto the map. This integrated visualization allows users to explore correlations between different factors and their impact on air quality. For instance, visualizing traffic patterns with pollution levels highlights the potential relationship between vehicle emissions and air quality deterioration.
- Interactive Exploration
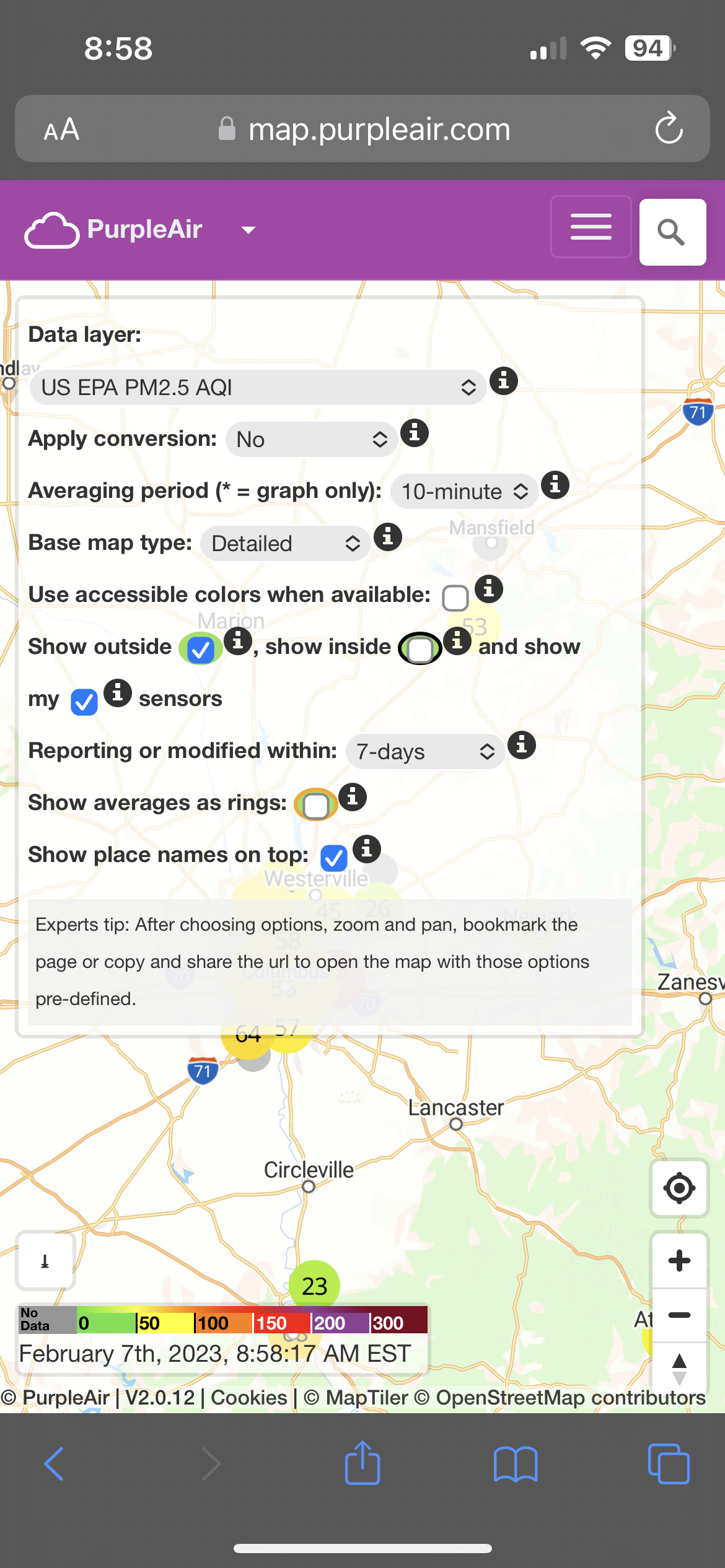
Modern data visualization, as exemplified by the PurpleAir map, often utilizes interactive features. Users can zoom, pan, and filter data according to specific time periods, locations, or pollutant types. This interactive exploration allows for detailed analysis of specific areas, providing more insights than a static visualization. Furthermore, selecting certain geographical locations can provide detailed, localized information on sensor readings, enriching the user experience and promoting more thorough data interpretation.
In conclusion, the effective visualization of data on the PurpleAir map is essential for users to readily grasp complex air quality information. This powerful tool transforms raw data into actionable insights, supporting public health initiatives, urban planning, and individual awareness regarding air quality, ultimately empowering individuals and organizations to make well-informed decisions about their environment. The clear visualization of pollution patterns and trends is essential for understanding potential risks, promoting effective interventions, and encouraging preventive measures.
7. Public access
Public access to the PurpleAir map is a fundamental aspect of its function. The map's value is directly tied to its availability to a broad audience. This accessibility empowers individuals and communities with real-time data on local air quality. Without widespread availability, the map's potential to inform public health decisions, support environmental monitoring, and foster public awareness of air quality issues would be significantly diminished.
Real-world examples illustrate the practical significance of public access. During periods of wildfire smoke, public access to real-time pollution data enables residents to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, such as adjusting outdoor activities, choosing protective measures, or knowing when to seek medical attention. Similarly, in urban areas experiencing industrial emissions, the public's ability to track and visualize pollution levels through the map contributes to informed community engagement, fostering awareness and accountability in managing pollution sources. The availability of this data fosters civic engagement, enabling citizens to actively participate in decisions pertaining to their environment and health.
In conclusion, public access to the PurpleAir map is not merely a feature but a defining characteristic of its value. It transforms air quality data from a specialized dataset into a public resource, facilitating a vital connection between scientific data and societal needs. This accessibility underscores the map's power to support informed decisions and foster community-driven environmental stewardship. Further development of tools that ensure public access in diverse formats and locations is critical for maximizing the map's potential and ensuring the broader benefits of readily available environmental data are realized.
PurpleAir Map FAQs
This section addresses common questions regarding the PurpleAir map, providing clear and concise answers for effective understanding of the tool's capabilities and limitations.
Question 1: What is the PurpleAir map?
The PurpleAir map is an interactive online tool that visualizes real-time air quality data. Utilizing a network of sensors, it displays current and historical pollutant levels across a specific geographical area, enabling users to identify pollution hotspots and track trends.
Question 2: How is data collected on the map?
Data is gathered from a vast network of air quality sensors. These sensors continuously measure various pollutants, such as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) and ozone. The network's data feeds into the map, presenting a comprehensive picture of current air quality conditions.
Question 3: What are the benefits of using the PurpleAir map?
The map's real-time data allows for swift identification of high-pollution areas, facilitating informed decisions. Users can monitor trends, understand seasonal variations, and make proactive choices to reduce exposure to pollutants. This information is valuable for individuals, public health organizations, and policymakers.
Question 4: Are the data on the map always accurate?
Data accuracy depends on several factors, including the reliability of individual sensors within the network. Maintenance, calibration, and sensor placement influence the accuracy of the readings. Users should always consider the data's potential limitations and cross-reference information with other sources when making critical decisions.
Question 5: What are the limitations of the PurpleAir map?
While providing valuable insights, the map's data represents a snapshot of air quality at specific locations. Gaps in sensor coverage may not reflect the entire area's air quality. Furthermore, the map does not always account for wind patterns and other dynamic factors affecting pollutant dispersal. Interpreting data with these limitations in mind is crucial.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of the PurpleAir map ensures responsible use and interpretation of the data presented, ultimately maximizing its value.
This concludes the frequently asked questions section. The following section will delve deeper into the practical applications of PurpleAir map data.
Conclusion
The PurpleAir map, through its real-time visualization of air quality data, offers a valuable resource for understanding and responding to environmental concerns. The map's interactive nature, coupled with its comprehensive sensor network, allows for the identification of pollution hotspots, trends, and patterns. This accessible tool empowers informed decision-making, supporting a variety of applications, including public health, urban planning, and environmental monitoring. The accuracy of the map's representation is contingent on the reliability and distribution of the sensor network, highlighting the need for robust data quality assessment. The visualization of data, encompassing spatial representation, temporal trends, and integration with other data sources, is crucial for translating complex information into actionable insights. Public accessibility further enhances the map's value, promoting community awareness and environmental stewardship. Careful consideration of the map's data limitations, including potential gaps in coverage and the dynamic nature of air quality, is essential for responsible interpretation and application.
The PurpleAir map represents a significant advancement in providing readily available, accessible, and comprehensive data for environmental monitoring. Continued development and enhancement of the sensor network, data visualization techniques, and data integration capabilities will contribute to a more complete and accurate picture of air quality. Furthermore, the ongoing evolution of data analysis methods and the integration of the map's data with other environmental monitoring systems will likely lead to even more powerful insights for proactive environmental management and public health protection. Ultimately, the ongoing development and responsible utilization of the PurpleAir map and similar technologies are crucial for effective and proactive environmental management in the future.
Purple Air Realtime Air Quality Map CLEAN EARTH FUTURE
Map Settings Data Layers PurpleAir Community
Monitoring Air Quality During Wildfires, in Partnership with PurpleAir